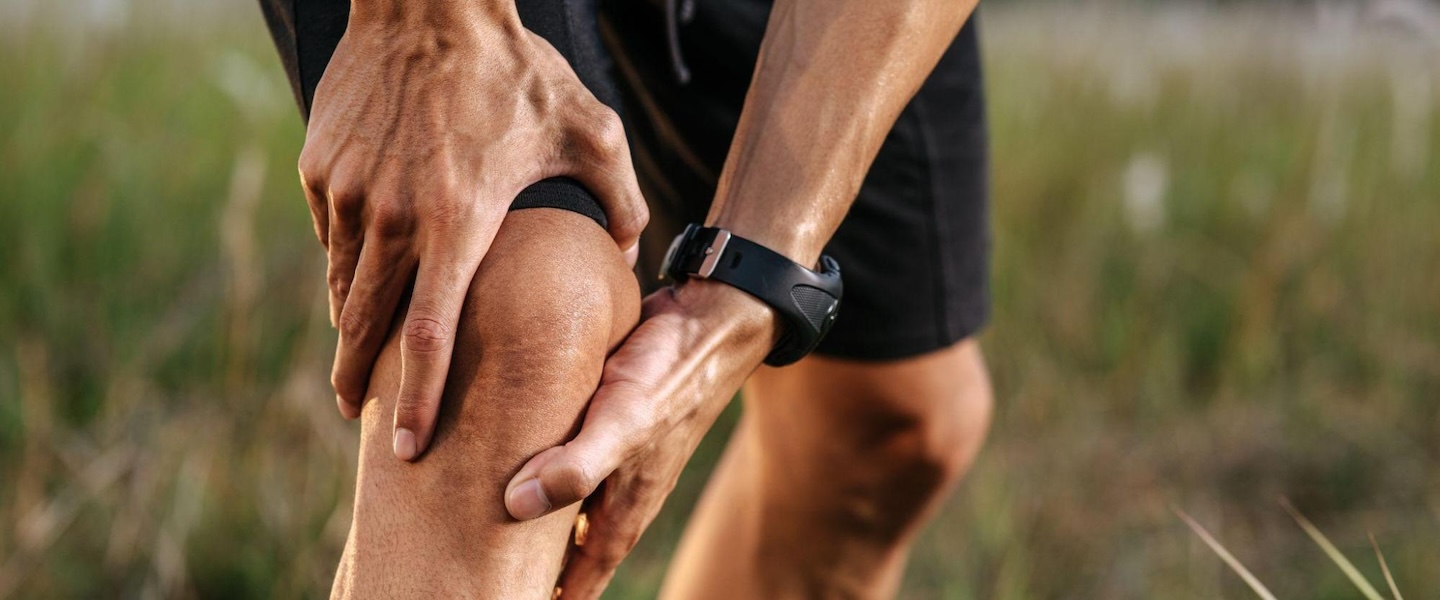
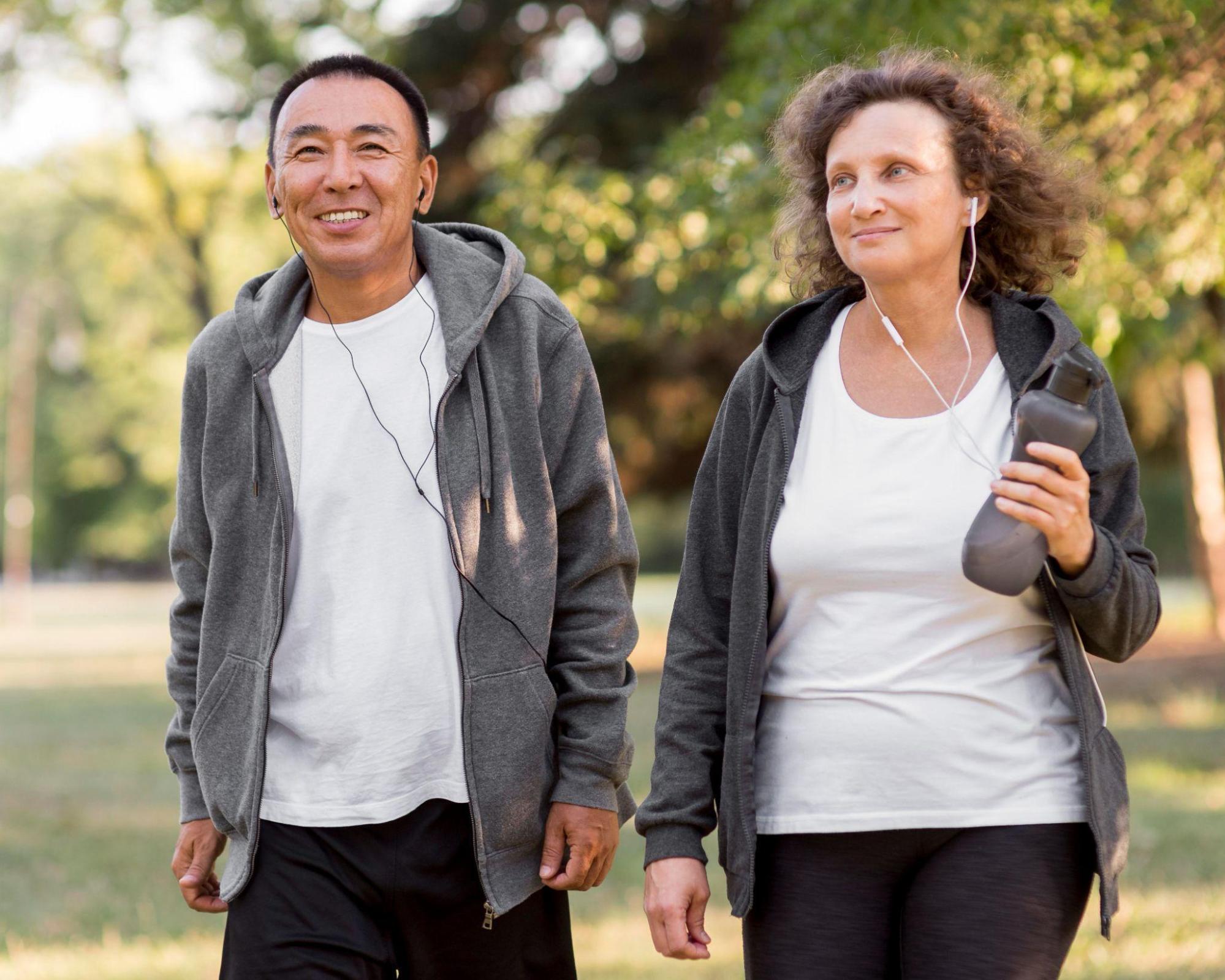
Osteoarthritis is a prevalent condition among older adults, affecting many worldwide. In Singapore, SingHealth reports that arthritis affects 10% of the population. It is considered a degenerative joint condition characterised by the breakdown of cartilage, which is the protective tissue that cushions the ends of bones within a joint. As the cartilage deteriorates, the bones rub against each other, causing pain, inflammation, and stiffness.
Common Joints Affected by Osteoarthritis
While osteoarthritis can affect any joint, symptoms most commonly occur in the following:
- Knees: Knee osteoarthritis could potentially be widespread and make walking, climbing stairs, and even standing for long periods difficult.
- Hips: Hip osteoarthritis could cause groin pain and limit hip movement, impacting daily activities like getting dressed and entering or exiting vehicles.
- Hands: Osteoarthritis in the hands could lead to pain, stiffness, and difficulty with fine motor skills, making tasks like buttoning a shirt or opening jars challenging.
- Spine: Osteoarthritis in the spine can increase the risk of back or neck pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion.
What Causes Osteoarthritis?
Although the exact cause of osteoarthritis remains unknown, there are several risk factors that contribute to its development:
- Gender: Women are more likely than men to develop osteoarthritis, especially after menopause.
- Age: The risk of osteoarthritis increases with age, particularly after 50.
- Prior Joint Injury: Injuries like fractures or ligament tears can increase the risk of osteoarthritis in the affected joint.
- Family History of Osteoarthritis: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to developing the condition.
- Being Overweight or Obese: Excess weight adds more stress on joints, particularly the knees and hips, accelerating cartilage breakdown.
- Repetitive or Excessive Joint Stress: Occupations or activities that expose joints to repetitive stress can contribute to osteoarthritis.
How to Manage Osteoarthritis in Older Adults
While there's no cure for osteoarthritis, several strategies can help manage its symptoms:
1. Exercise for Joint Health
Regular exercise is crucial for managing osteoarthritis. Low-impact exercises like swimming, cycling, and walking can support joint flexibility, strengthen surrounding muscles and potentially mitigate the risk of having to deal with pain-related symptoms. Engaging in consistent physical activity can also enhance overall physical fitness, which is beneficial for joint health.
Working with physical therapists can be particularly advantageous, as they can design personalised exercise programmes tailored to individual needs and abilities. This ensures that you have exercises that are right for your fitness level and condition.
2. Maintaining a Healthy Weight
As excess weight places additional strain on weight-bearing joints, it's important to manage weight to help joint function. Collaborating with a registered dietitian can help create a healthy meal plan that supports weight management. They can help you develop one focusing on foods that provide the vitamins and minerals needed for overall health.
3. Collaborative Management with a Doctor
Doctors can assess the progression of osteoarthritis, recommend appropriate solutions to address your symptoms and monitor for any complications. These may include medications for pain management and inflammation, physical therapy, and possibly surgical interventions for severe cases.
Having an open line of communication with healthcare providers ensures that any changes in symptoms or new challenges are promptly addressed.
4. Proper Joint Protection
Protecting joints from excessive stress is crucial for slowing osteoarthritis progression. This can involve:
- Using assistive devices: Canes, walkers, or braces can provide support and reduce stress on affected joints, making daily activities easier and safer.
- Maintaining good posture: Proper posture can help in supporting your joints, particularly the spine. Ergonomic adjustments to workspaces and living environments can help with maintaining good posture and potentially minimise joint strain.
5. Consider Joint Support and Osteoarthritis Supplements
Consider asking your doctor if joint support supplements are suitable for your condition. Joint support supplements, particularly osteoarthritis supplements with glucosamine, chondroitin, and methylsulfonylmethane (MSM), can potentially help in supporting your cartilage health.
Glucosamine and chondroitin are natural chemical compounds that can be found in your body, but they can also come in the form of a supplement. There have been research studies that showed that they have anti-inflammatory properties that can help with pain management for osteoarthritis. They have also been shown to protect cells known as chondrocytes, which help with cartilage structure. On the other hand, researchers found that MSM has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that support symptom management for those with osteoarthritis. It also helps in the production of collagen and glucosamine, which are essential for bone and joint function.
Live Life to the Fullest Even with Osteoarthritis
While osteoarthritis can present significant challenges, it doesn't have to define one’s golden years. With a proactive and informed approach, managing this condition is possible. By partnering with healthcare professionals in Singapore and staying informed about proper osteoarthritis management approaches, older adults can live a life that's not only comfortable but also active and fulfilling.
For more health and ageing insights, check out how you can find joy and purpose in your 50s and how to manage your blood sugar levels.